Notes from a presentation by https://twitter.com/mgroves . Replay available https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5Cjdv38sS_yNEue-QUAF7g
Agenda:
- Why NoSQL?
- JSON Data Modeling
- Accessing Data
- Migrating Data
- Summary / Q&A
Why NoSQL
"Change is inevitable" and relational databases don't handle change as well. NoSQL databases scale much easier
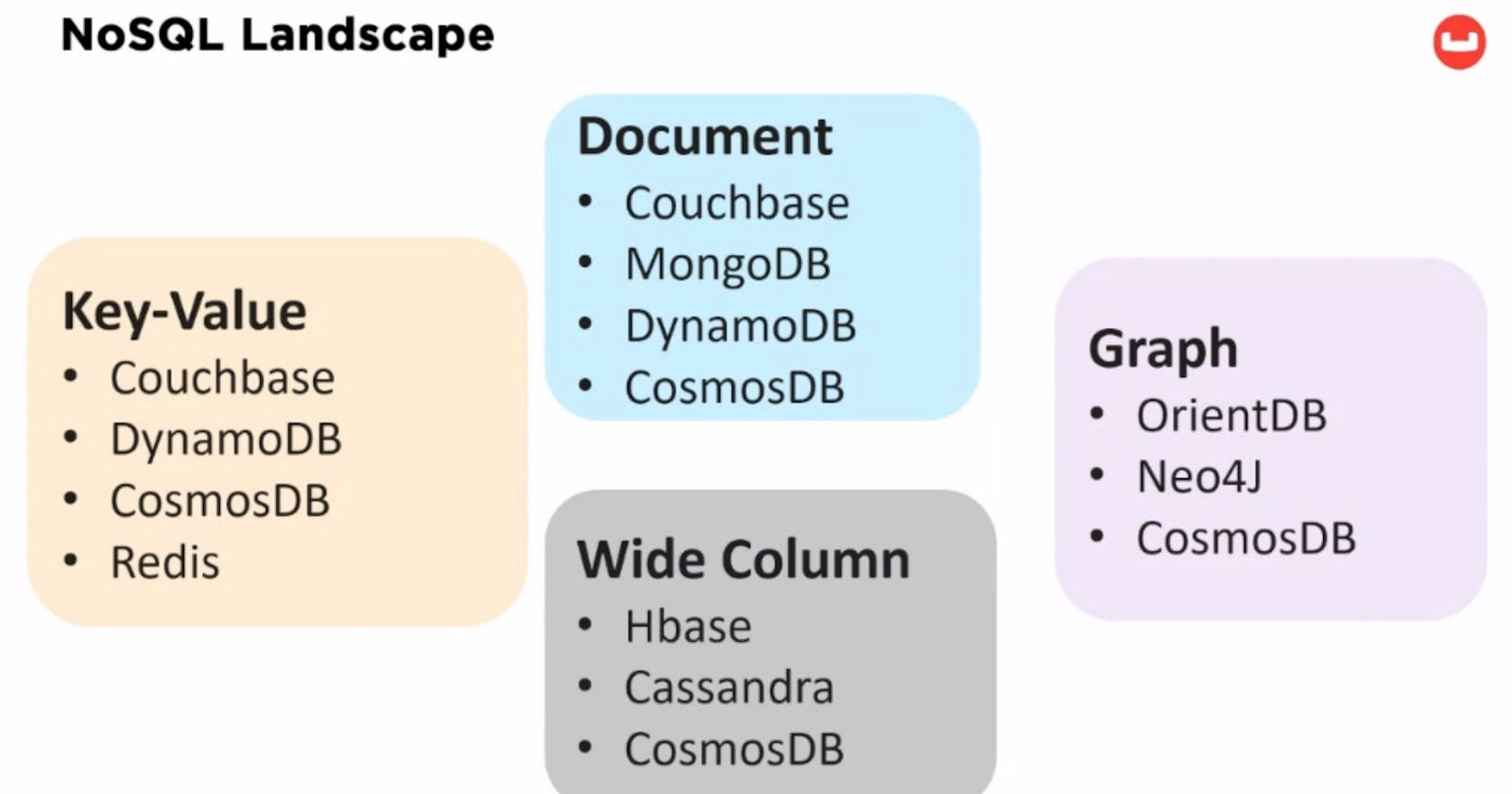
Types of NoSQL Databases:
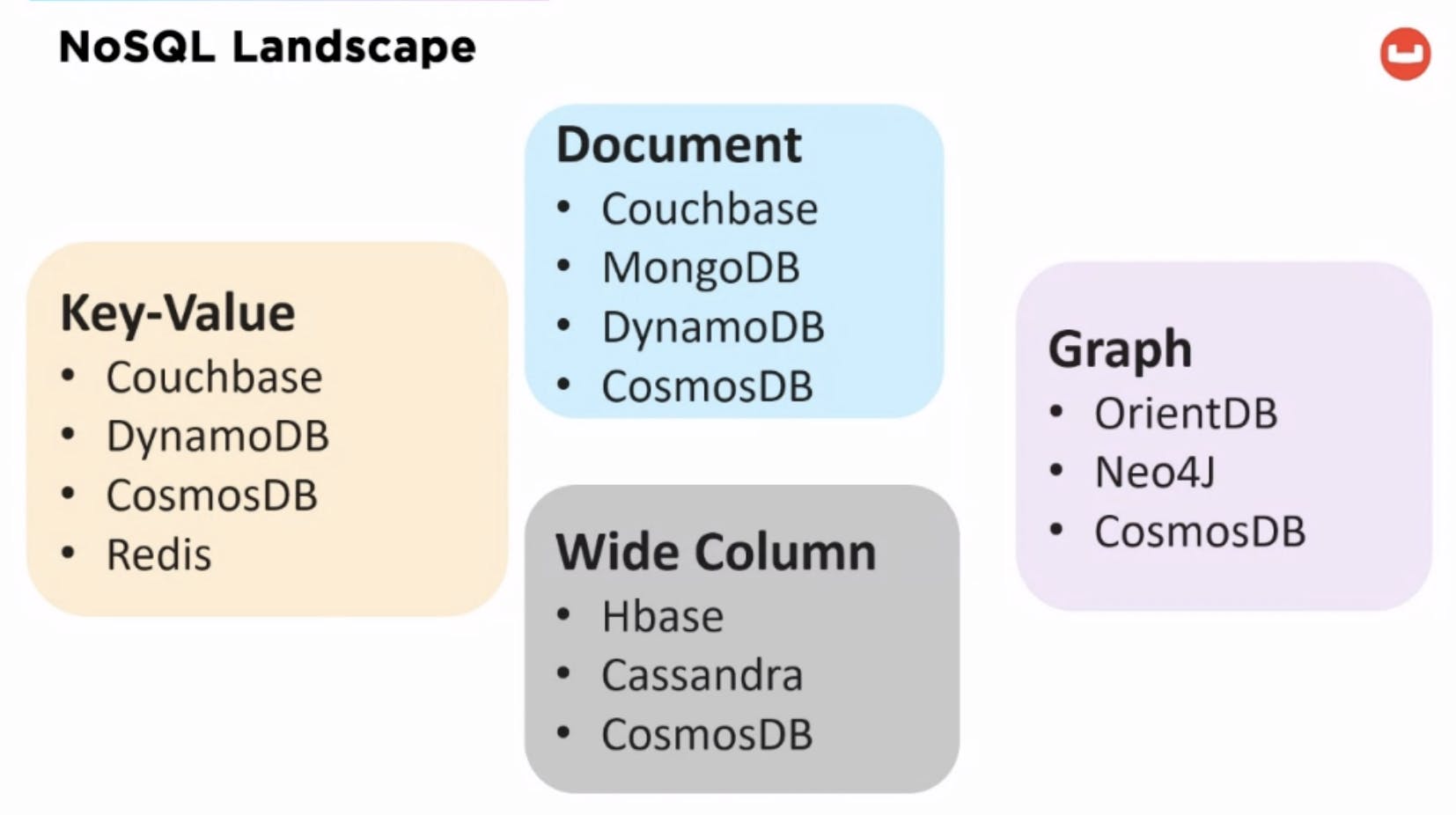
Document DB
- Get, Set, Replace, Delete by key(s) Simplest type of a key-value store Scalability comes in the form of multiple nodes in a cluster
No inherent relationship between data. Provides flexibility
Performance
Use Cases: Caching, session, user profile, content management Other users: gaming, advertising, travel booking, loyalty programs, fraud monitoring, social media, finance, customer 360, IoT, communication
JSON Data Modeling
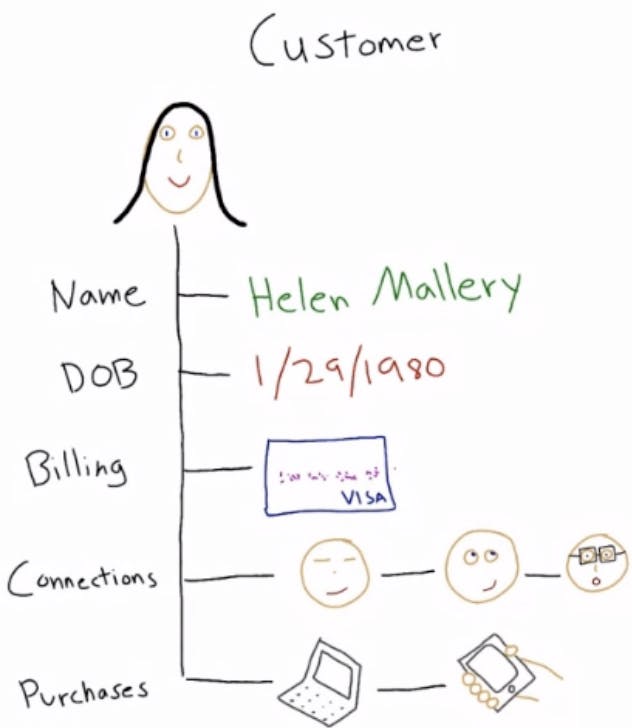
Properties of Real-World Data: example: customer
- Name
- DoB
- Billing
- Connections
- Purchases
The old way of relational databases:
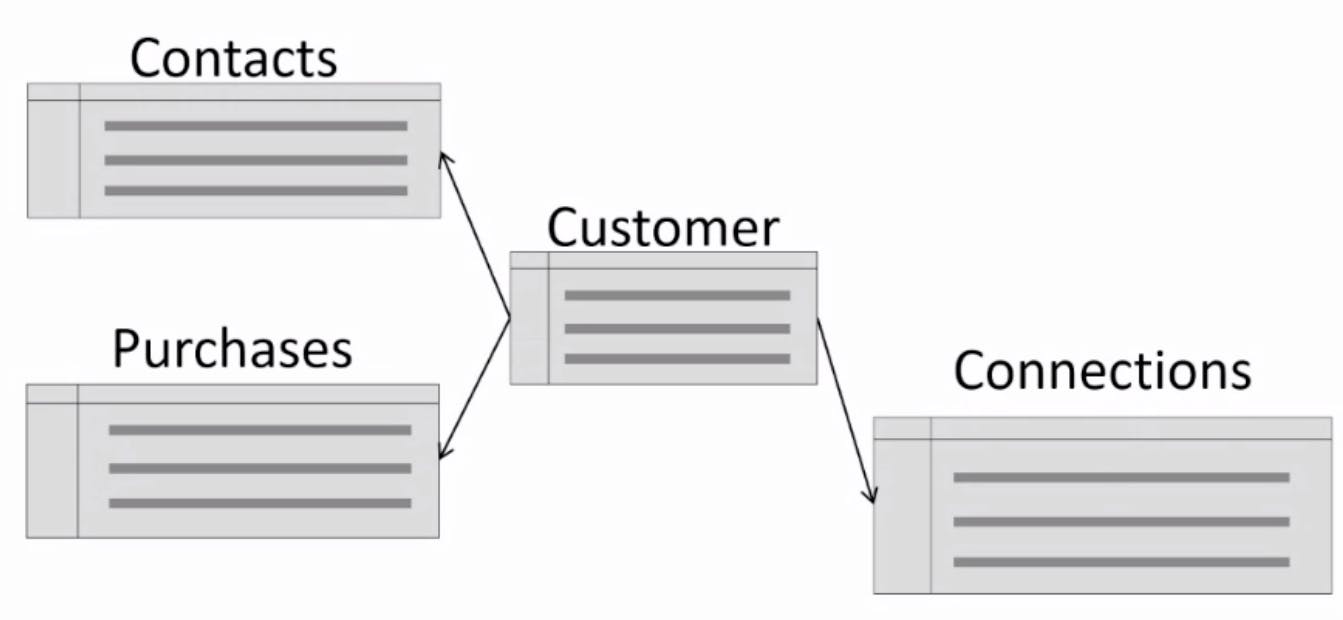 As schemas get more complex, it gets harder to add tables and columns.
As schemas get more complex, it gets harder to add tables and columns.
RDBMS vs DocumentDB:
Standard Customer table:
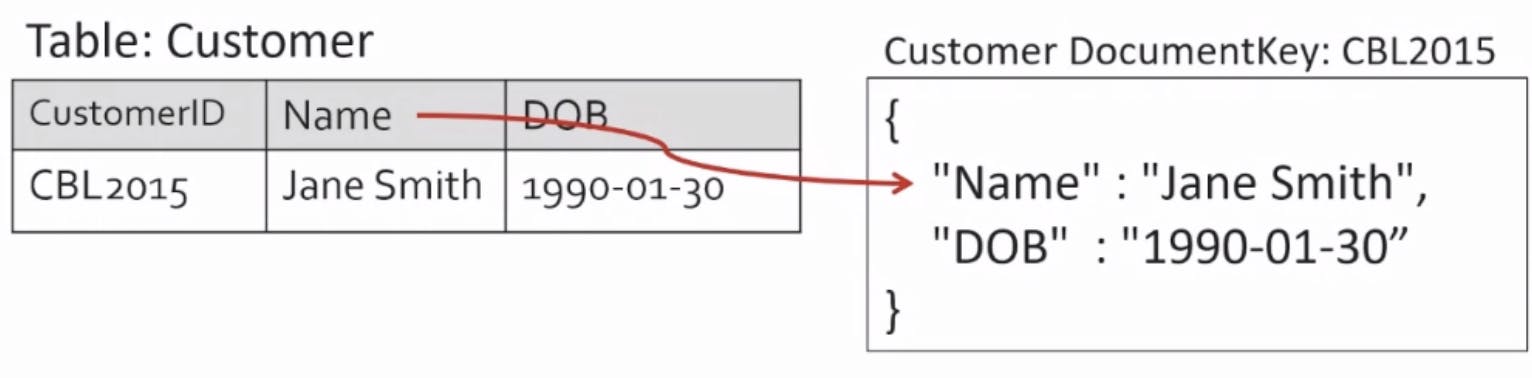
Introduce another table:
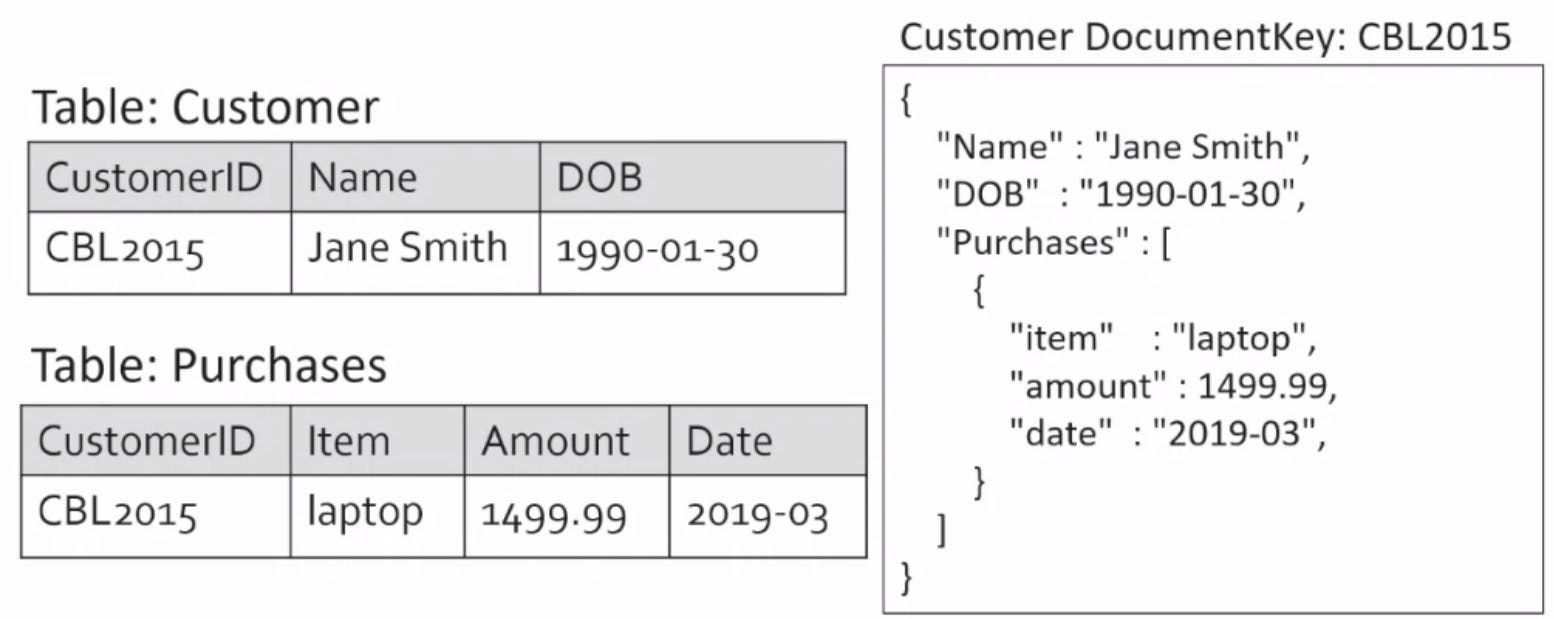
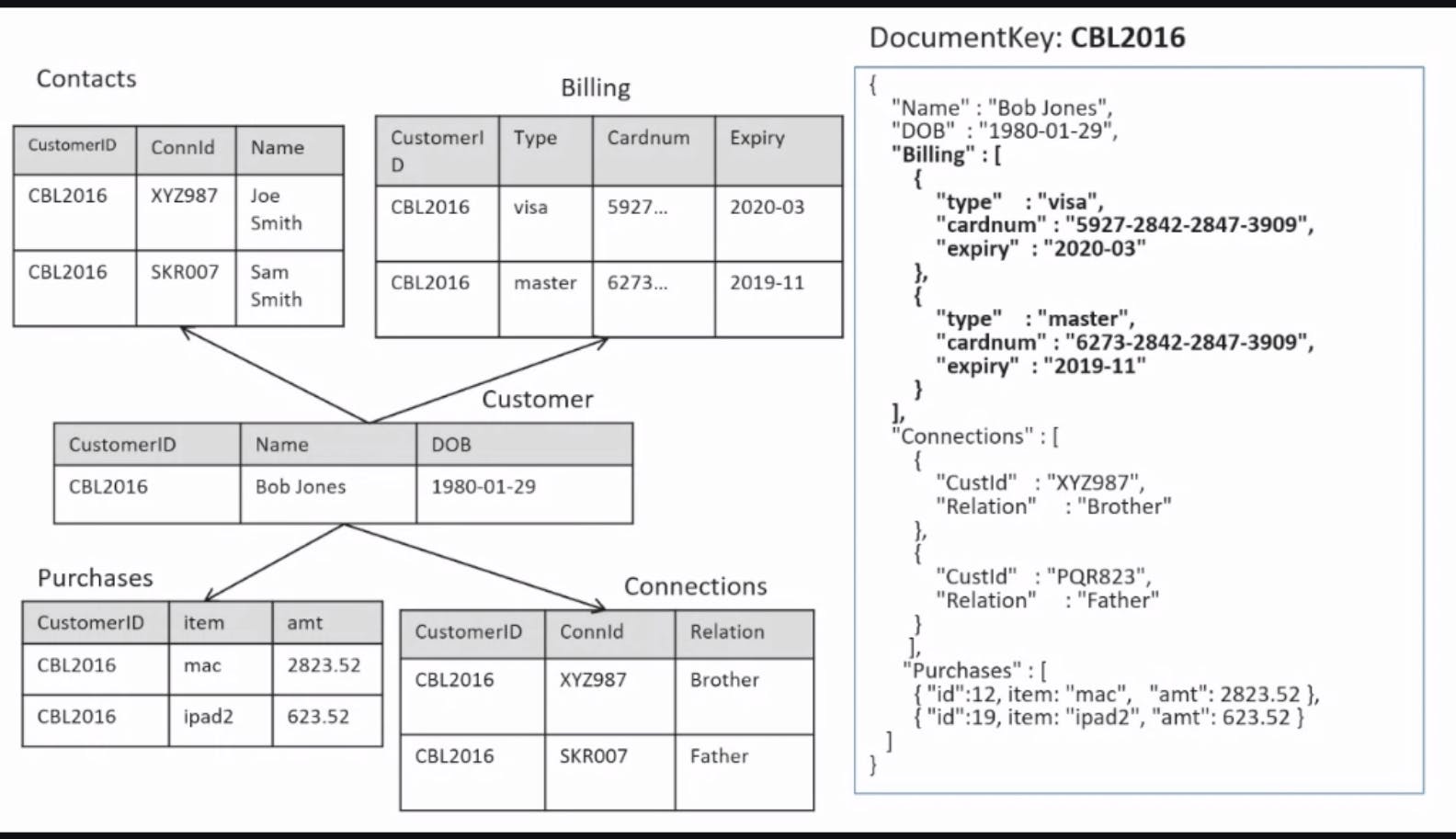
RDBMS would require a "Join" at this point, but with the document model, it's still just one piece document
Adding more rows is easy by adding items to the array
(quotes are not optional for valid JSON)
Creating the connections array refers to another document with a documentkey ID.
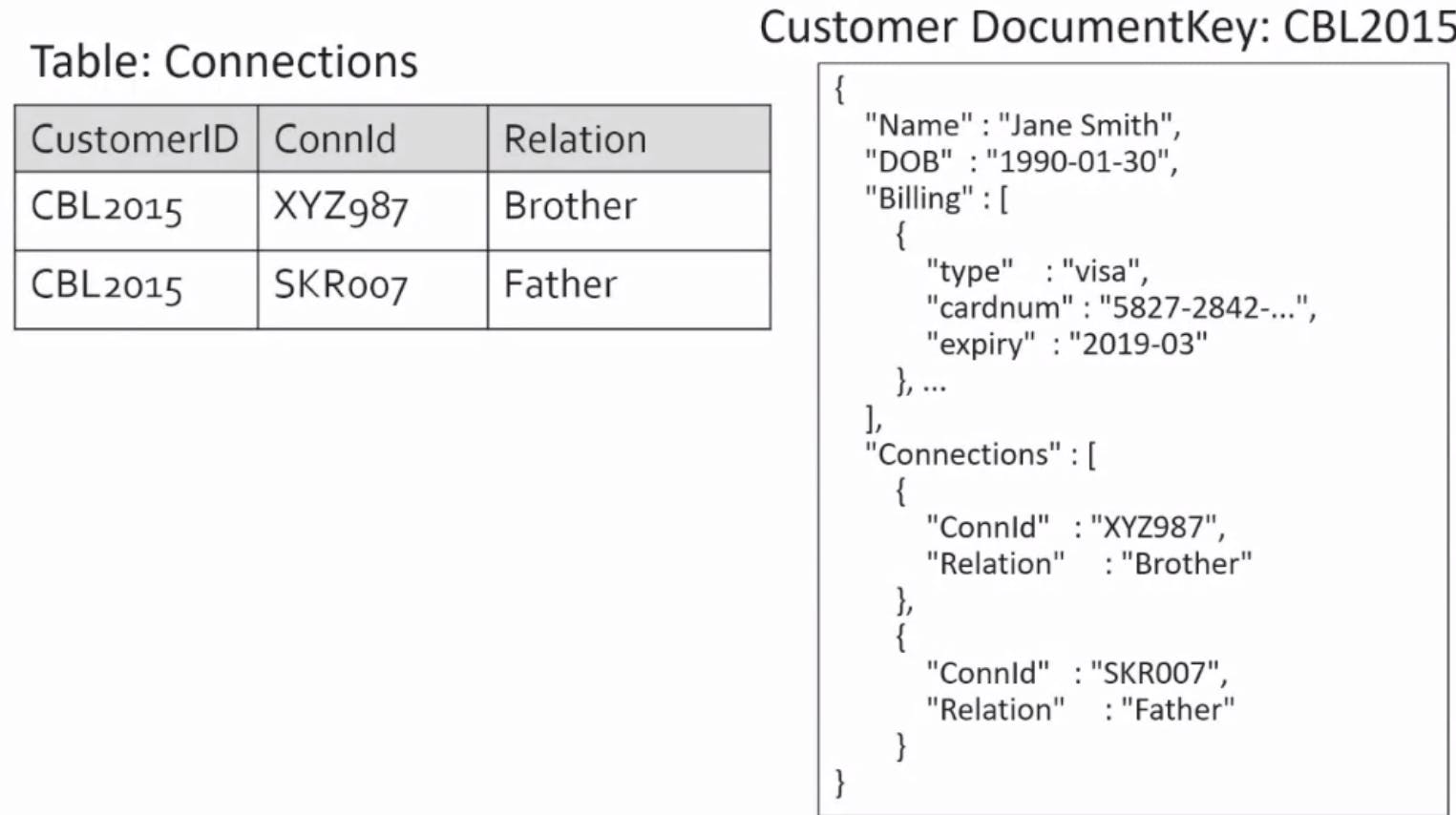
The full model:
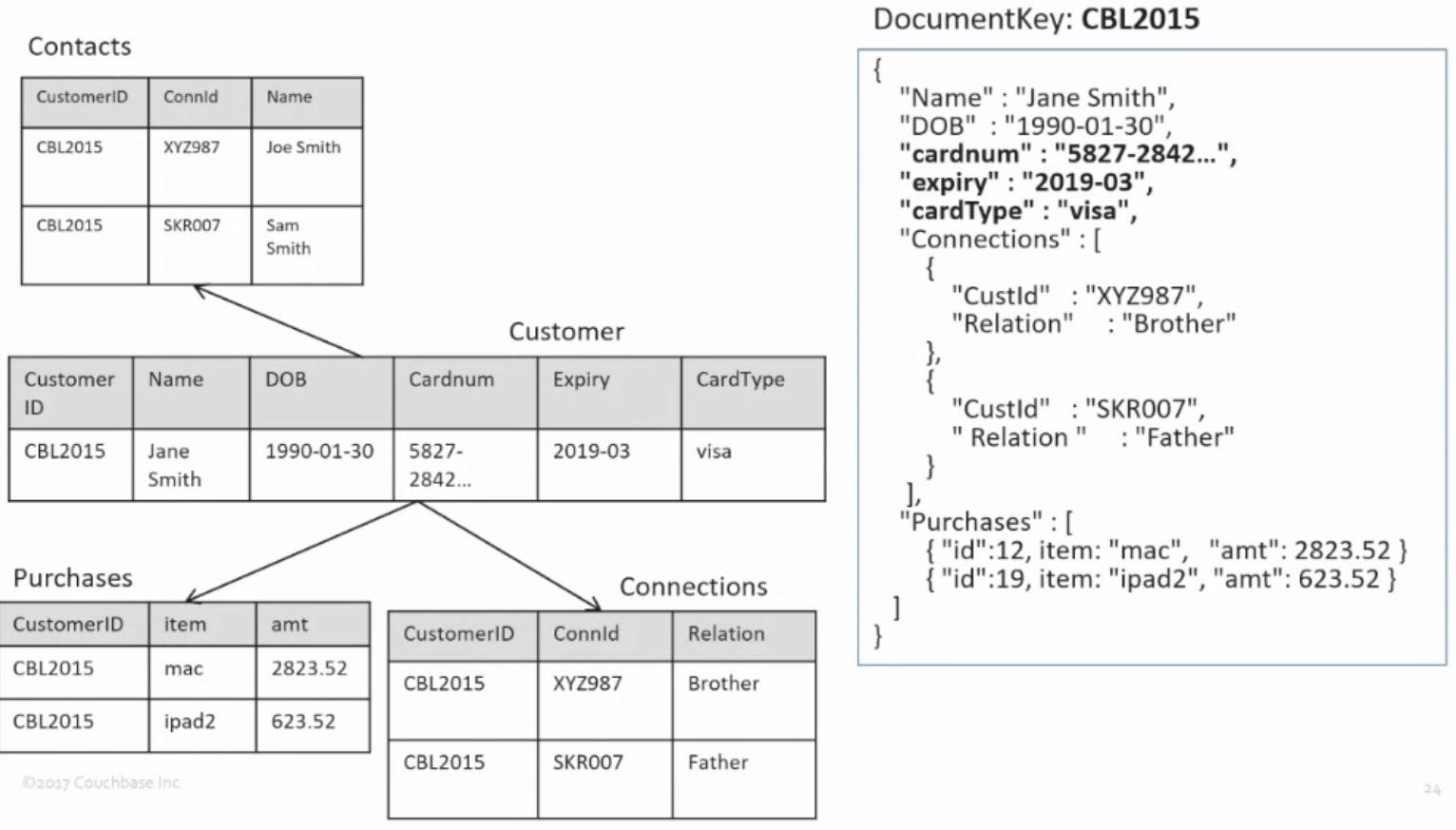
Ways to control documents: You can version documents with different ways to break out the model Does not require a change to pk or fk.

Can also reversion with a web application. Get data from old document and save it to the new (user initiated)
Tools to help with modeling

jsoneditoronline.org is the only free one.
Accessing Data
SQL is accessed via SQL Query. NoSQL has many many options to access. -
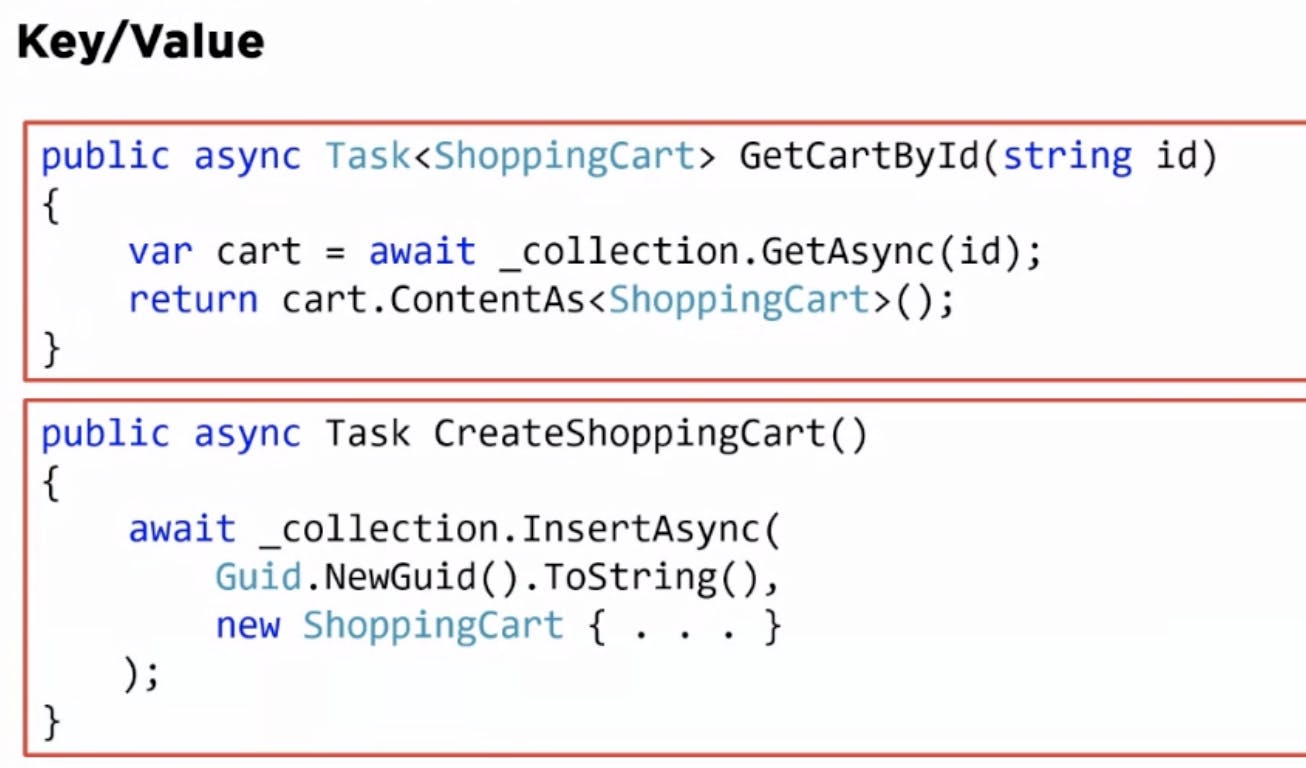
Example using C#:
Recommendations for keys:
- Natural Keys (something that has a value that makes sense, but that won't change)
- Human Readable
- Deterministic
- Semantic
Deterministic means that a "march" through the data makes sense.

Example: Find author, pull up author's blogs, go to blog posts, pull blog posts comments
Relationships:
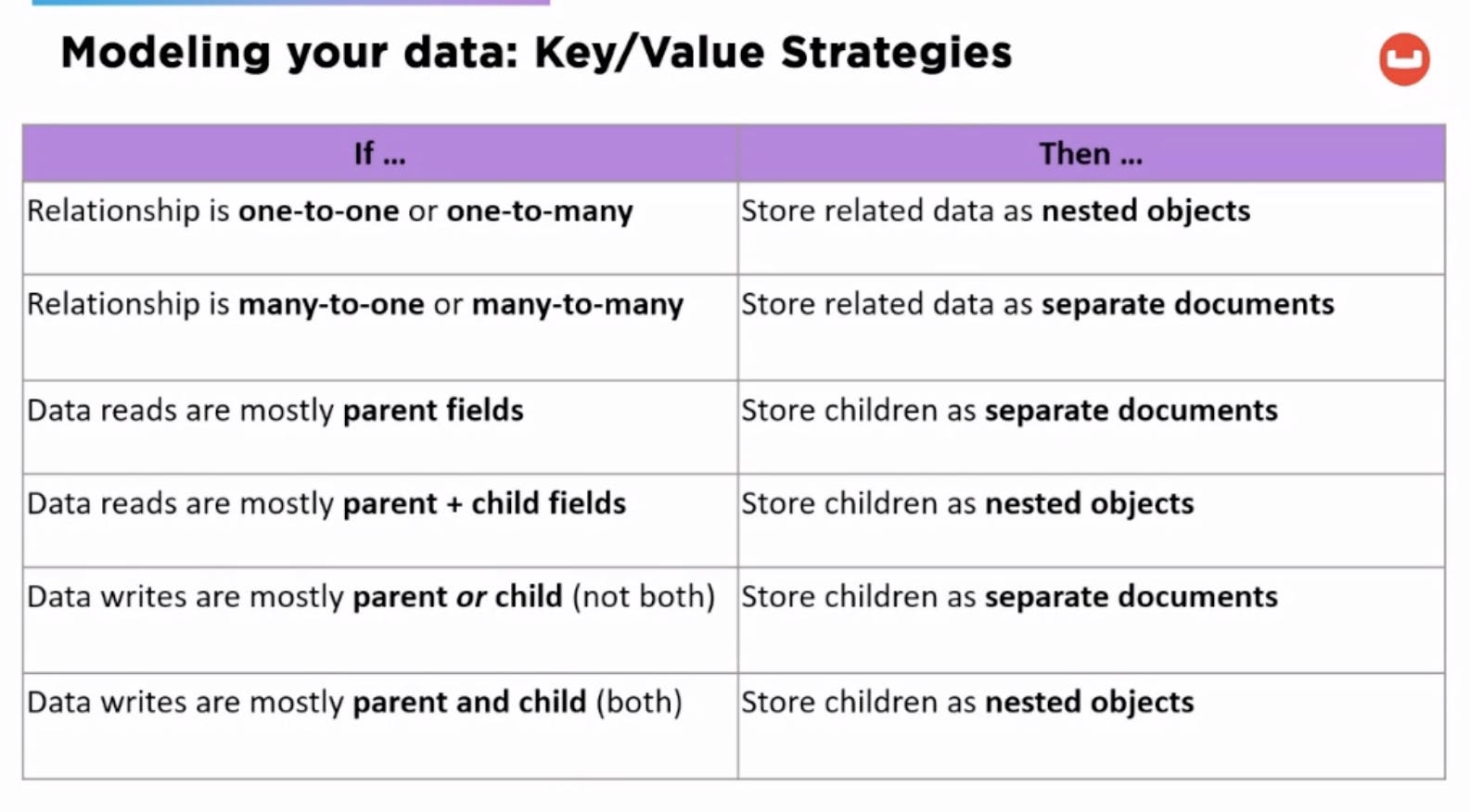
Subdocument Access (API)
Update via subdocument api, can speed up updates without accessing the whole document
Other ways to access the data
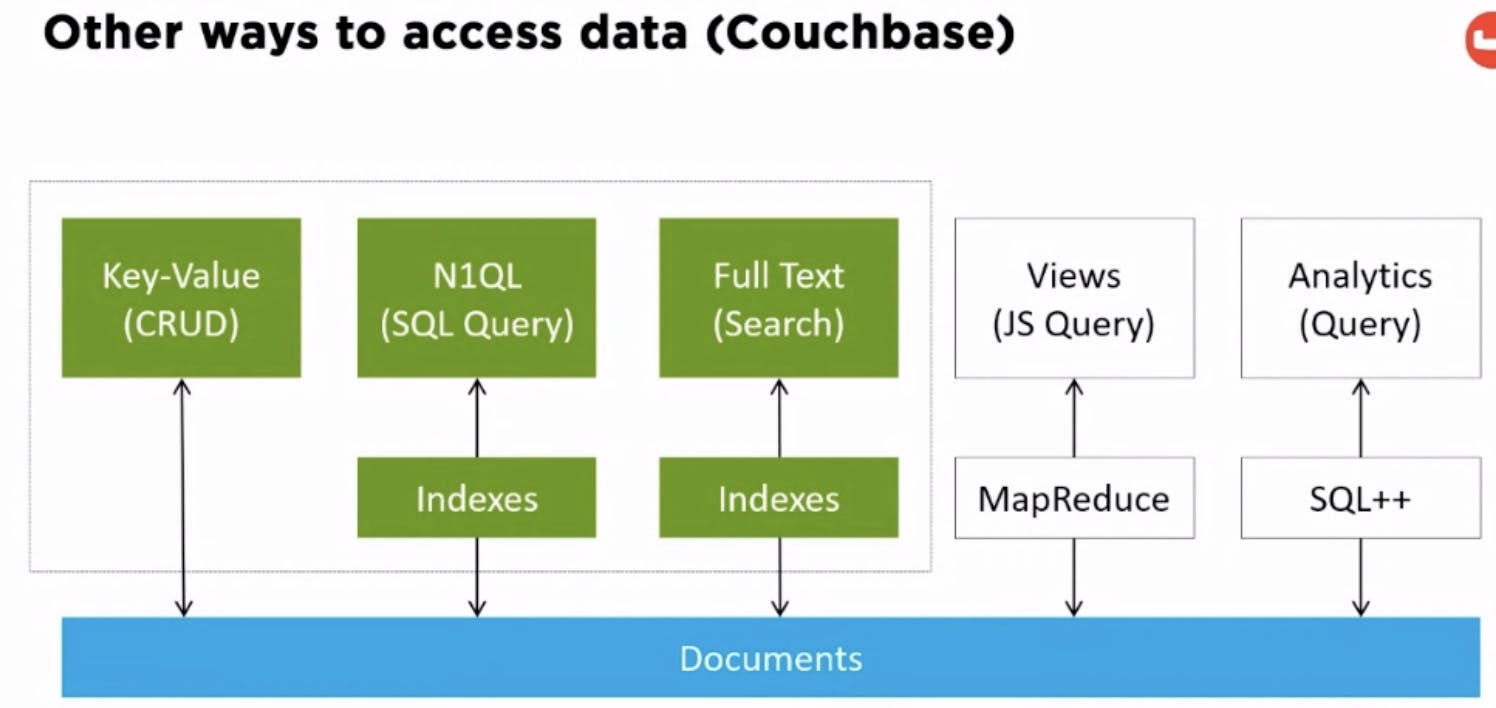
N1QL (SQL for Document DB) Example:
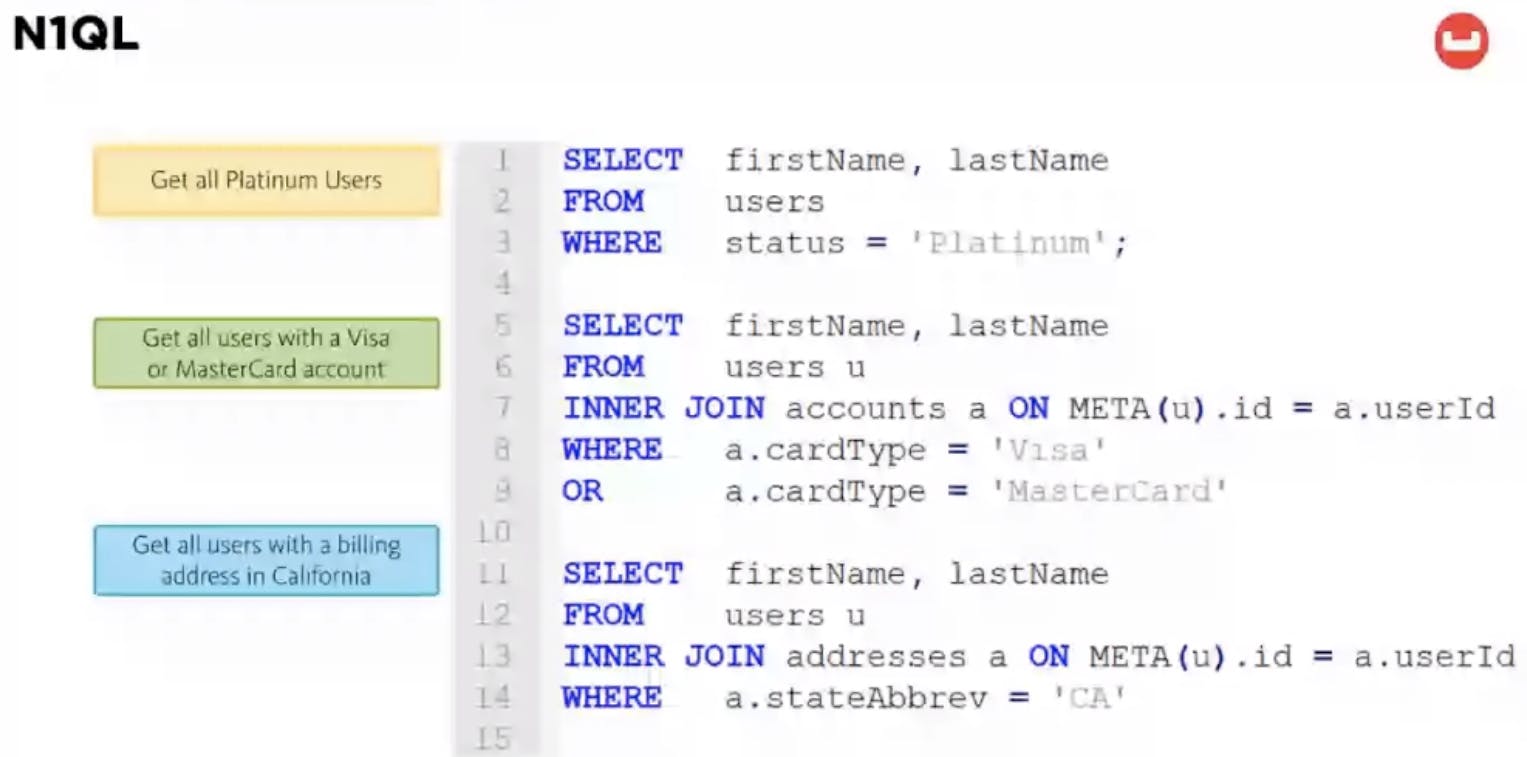
Search with index and use suggestions to improve performance.
Full Text Search - find all the results that have the word you're looking for
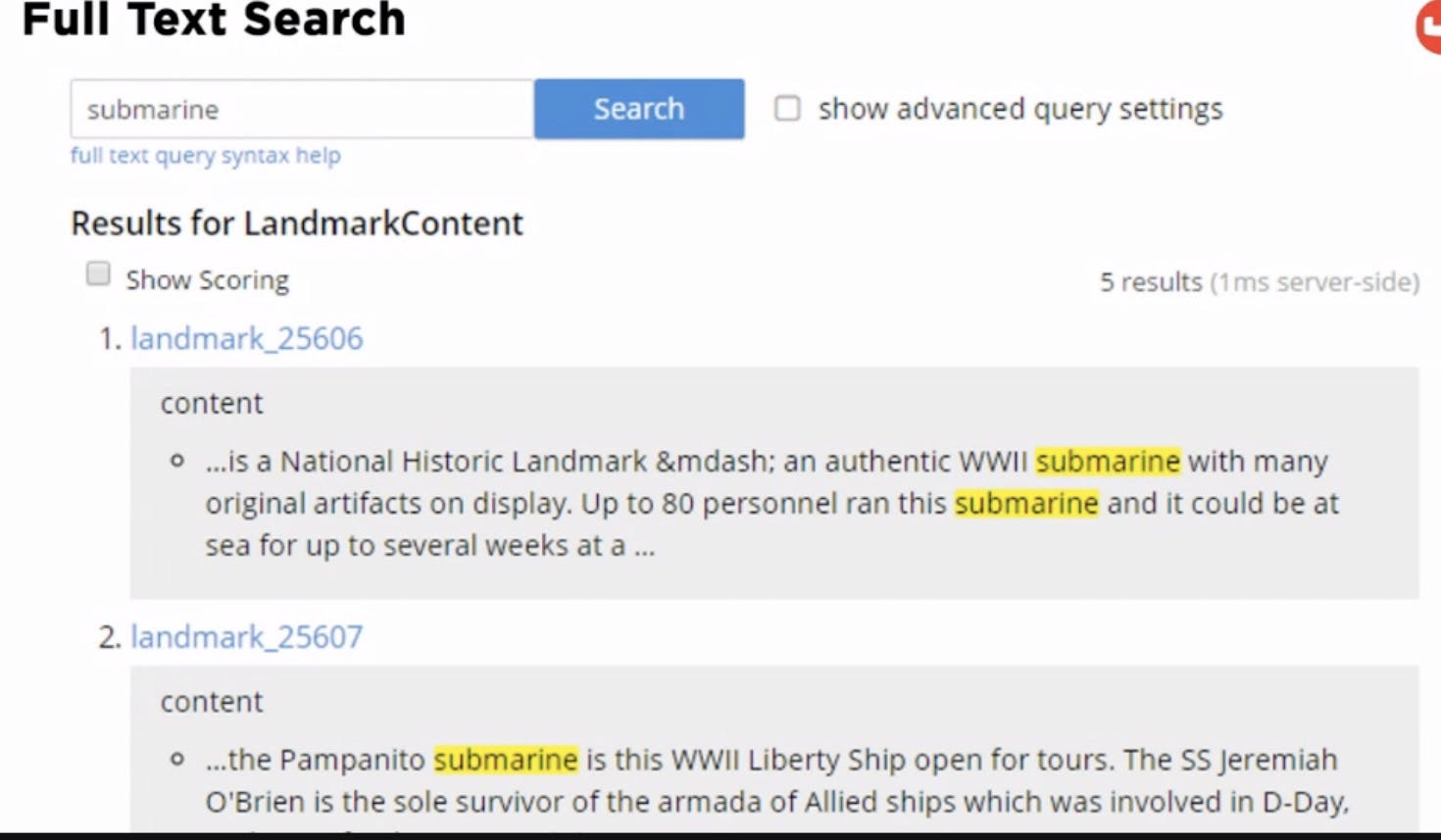
Good for lots of things like inverted index, geographical
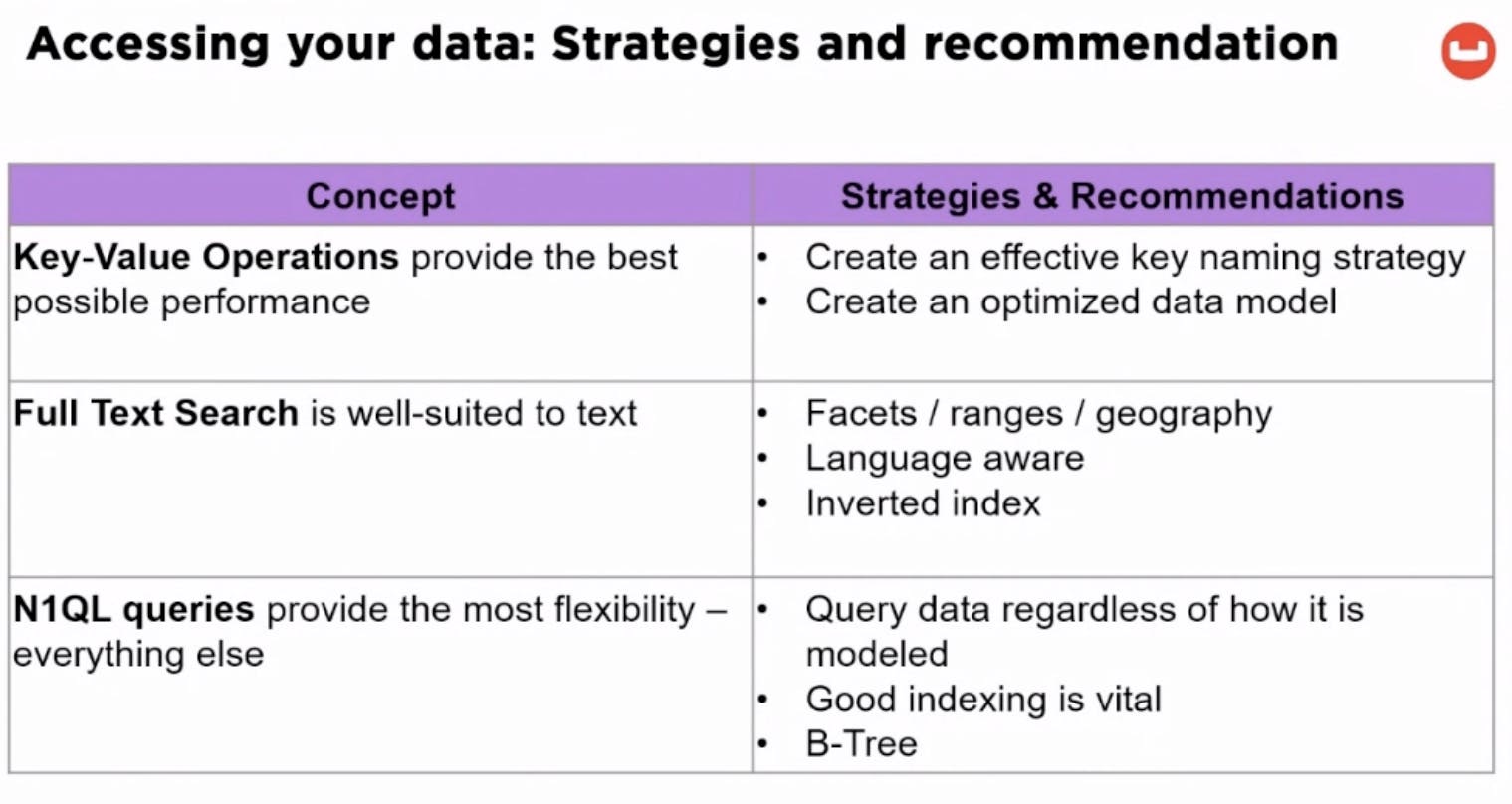
Use the right concept to access the data, and model the data accordingly.
Migrating

Tools:


Do it with a simple CSV output and import. Once data is in place, start using or transforming that data into a future state.
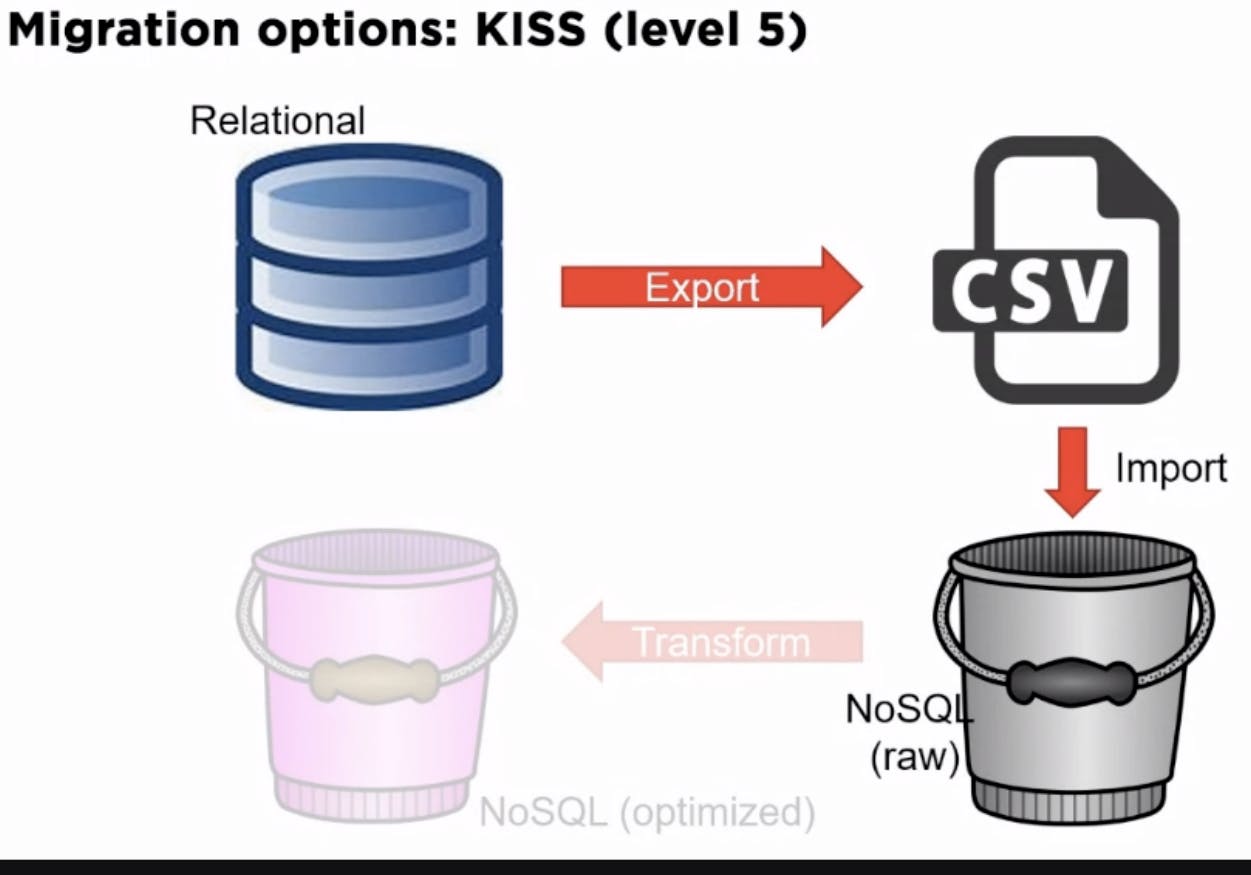
Align your data with the ways you want to access it.
CouchBase ships with samples.
DEMO
Demo showed creating a bucket and running a C# program to convert the data from SQL Server to Couchbase. Bucket contains Scopes, Scopes contain collections, collection contains documents
Take Away
- Pick the right application
- Proof of concept
- Match the data access method to the requirements
- Links: blog.couchbase.com/sql-to-nosql-automated-m.. blog.couchbase.com/proof-of-concept-move-re.. missed the last one